Search results
Directory:
Tags:

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 1 comment
1 comment
Directory:
Tags:
|
Directory:
Tags:

- CanRisk is a new online gene-based health-risk evaluation algorithm for detecting breast cancer
- It identifies people with different levels of risk of breast cancer, not just those at high risk
- As the infotech and biotech revolutions merge expect authority in medicine to be transferred to algorithms
- CanRisk has the potential to provide a cheap, rapid, non-invasive, highly sensitive and accurate diagnosis before symptoms present
- Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women worldwide and is the 5th most common cause of death from cancer in women
- Currently mammography screening, which has a sensitivity between 72% and 87%, is the gold standard for preventing and controlling breast cancer
- For every death from breast cancer that is prevented by screening, it is estimated there will be three false-positive cases that are detected and treated unnecessarily
- Lack of resources do not support breast cancer screening in many regions of the world where the incidence rates of the disease are rapidly increasing
- In the near-term expect interest in the CanRisk algorithm to increase
A new comprehensive gene-based breast cancer prediction device
A new online gene-based health-risk evaluation device called CanRisk has the potential to identify women with different levels of risk of breast cancer; not just women who are at high risk. Predicated on a comprehensive algorithm, CanRisk is one of several innovations currently in development, which include novel methods for predicting the recurrence of breast cancer, a new class of molecules that aim to halt or destroy breast cancer, and liquid biopsies, which determine the presence and recurrent risk of the disease through the detection of tumour cells in peoples’ blood.
Although over the past two decades there have been significant improvements in the detection and treatment of breast cancer, the disease remains the most common cancer in women worldwide, with some 1.7m new cases diagnosed each year, which account for about 25% of all cancers in women and it is the fifth most common cause of death from cancer in women, with over 0.52m deaths each year.
Although over the past two decades there have been significant improvements in the detection and treatment of breast cancer, the disease remains the most common cancer in women worldwide, with some 1.7m new cases diagnosed each year, which account for about 25% of all cancers in women and it is the fifth most common cause of death from cancer in women, with over 0.52m deaths each year.
Game changer for breast cancer
Findings of CanRisk were reported in the January 2019 edition of Genetics in Medicine. Findings of a less comprehensive version of the device’s algorithm were published in the July 2016 edition of the same journal. Commenting on the 2019 study, Antonis Antoniou, Professor of Cancer Risk Prediction at the University of Cambridge and lead author of the two studies said: "This is the first time that anyone has combined so many elements into one breast cancer prediction tool. It could be a game changer for breast cancer and help doctors to tailor the care they provide depending on their patients' level of risk”.
When fully developed and approved, CanRisk will be well positioned to provide a cheap, rapid, non-invasive, highly sensitive and accurate diagnostic test to detect breast cancer early in people with diverse levels of risk. This might be expected to provide an alternative to the current gold standard population-based mammography screening and assist in making a significant dent in the vast and escalating global burden of the disease.
When fully developed and approved, CanRisk will be well positioned to provide a cheap, rapid, non-invasive, highly sensitive and accurate diagnostic test to detect breast cancer early in people with diverse levels of risk. This might be expected to provide an alternative to the current gold standard population-based mammography screening and assist in making a significant dent in the vast and escalating global burden of the disease.
In this Commentary
This Commentary describes the algorithm that drives CanRisk, which benefits from the increasing availability of vast and growing amounts of genomic and other personal data and significant advances in genomic sequencing technologies. The confluence of these two phenomena facilitates and enhances the quality and speed of data analysis and drives the development of new and innovative diagnostic and prognostic cancer technologies. The fact that CanRisk is based on UK data and its algorithm is available to researchers globally, presents a potential opportunity for medical research organizations in emerging regions of the world where the burden of breast cancer is increasing. The Commentary briefly describes the heterogeneous nature of breast cancer and highlights some of its complexities and risk factors. Originally perceived as a Western disease, breast cancer is growing rapidly in Asia and other regions of the world where it tends to be detected late and managed less effectively. Developed economies prevent and manage breast cancer through well-established population-based mammography screening programs. Because of the lack of resources, such screening programs are not widely available in low to middle income countries (LMIC). As the infotech and biotech revolutions merge expect authority in medicine to be transferred to Big Data algorithms such as CanRisk. This not only could provide an alternative to gold standard mammography screening, but also provide a cheap and effective device for use in developing nations where the burden of breast cancer is significant and increasing.
CanRisk: a world first
CanRisk, developed by members of the Centre for Cancer Genetic Epidemiology at the University of Cambridge, UK, takes advantage of discoveries in both cancer genomics and epidemiology and aims to become a popular device used by primary care physicians, in consultation with their patients, to effectively assess patients’ diverse levels of risk of developing breast cancer. The device is predicated on an algorithm called BOADICEA (the Breast and Ovarian Analysis of Disease Incidence and Carrier Estimation Algorithm). This is the world’s first polygenic breast cancer risk model and the only one to-date, which is available to the international research community. Also, it is the first breast cancer risk model to incorporate pathology data and population-specific cancer incidences in risk calculations. The algorithm accounts for over 300 genetic risk factors, including BRCA1, [BReast CAncer gene] BRCA2, PALB2, CHEK2, and ATM, which are genes that have been found to impact a person’s chances of developing breast cancer. The device uses a Polygenic Risk Score (PRS) based on 313 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), [SNPs, pronounced ‘snips’, are the most common types of genetic variation in people. Each SNP represents a difference in a single DNA building block and is called a nucleotide] which explains 20% of breast cancer polygenic variance. CanRisk also includes a residual polygenic component, which accounts for other genetic/familial effects; known lifestyle/hormonal/reproductive risk factors and mammographic density [Dense breast tissue can make it harder to evaluate mammographic results and may also be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer].
|
|
|
|
Directory:
Tags:

|
|
|
Directory:
Tags:

|
|
|
Directory:
Tags:

|
|
|
|
|
Directory:
Tags:

|
Directory:
Tags:

|
Directory:
Tags:

- Narayana Hrudayalaya (NH) is an innovative Indian healthcare provider
- In just 15 years NH has become one of India’s leading hospital groups
- Founded by Dr Devi Shetty, a heart surgeon, NH treats nearly 2m patients a year
- NH has built an international reputation for affordable quality healthcare
- A number of large institutional investors are betting that NH can grow
- Is NH’s model of affordable quality healthcare replicable outside of India?
Will Devi Shetty have a major influence on global healthcare?
PART 1
Dr. Devi Shetty, founder and chairman of Narayana Hrudayalaya (NH), an innovative Indian healthcare provider, wants to transform the way healthcare is delivered across the world. Can he do it?
This Commentary is in three parts. Part 1 is a general introduction to NH and its 2015 initial public offering. It describes some of NH’s internal challenges and suggests that it is reasonable to assume that these will be overcome given its position within a buoyant Indian healthcare market. Part 2 describes some key aspects of NH’s model for affordable quality healthcare. In particular, it shows how Shetty has embraced information technology and some aspects of scientific management to create mega hospitals in India that delivers sustainable high-volume affordable quality care. Part 3 discusses some of the challenges associated with replicating the NH model outside of India. It briefly describes Shetty’s initiative to create a medical city in the Cayman Islands to capture share from the North and South American healthcare markets. It discusses some of the barriers to replicating the model in the UK and other developed markets and suggests that besides India; Africa, - despite its complexities and challenges - might offer NH growth opportunities. It also suggests that NH could play a leading role in training a new generation of healthcare professionals specifically attuned to the vast and escalating healthcare needs of developing economies, and this could be commercially valuable.
London-based financial institution CDC and a number of others think Shetty can provide the world with a new model of affirdable healthcare. In December 2015 the CDC Group, owned by the British government, with an investment portfolio valued at £2.8bn, backed NH’s initial public offering (IPO) with an investment of US$48m. The IPO valued NH at US$1bn. The issue was 8.6 times oversubscribed, with most of the demand coming from foreign institutional investors. Beside CDC, other anchor investors included the government of Singapore, Morgan Stanley, Nomura, BlackRock, and Prudential.
Dharmesh Mehta, former managing director and CEO of Axis Capital, one of the bankers to the issue, said: “We got one of the best anchor books, with several long-term investors supporting it. Investors are bullish about the Indian healthcare space, especially hospitals, and Narayana Hrudayalaya has a unique business model, and the backing of good quality management.”
In the video below Shetty argues that, “Healthcare of the future will not be an extension of the past.” Shetty has a good understanding about how technology is revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered and changing its structure and organization to such an extent that the future of healthcare will be dramatically different from what it is today. Healthcare is moving beyond the hospital towards patient self-knowledge and empowerment. Home-healthcare services facilitate enhanced doctor-patient connectivity where it had not been previously possible.
This Commentary is in three parts. Part 1 is a general introduction to NH and its 2015 initial public offering. It describes some of NH’s internal challenges and suggests that it is reasonable to assume that these will be overcome given its position within a buoyant Indian healthcare market. Part 2 describes some key aspects of NH’s model for affordable quality healthcare. In particular, it shows how Shetty has embraced information technology and some aspects of scientific management to create mega hospitals in India that delivers sustainable high-volume affordable quality care. Part 3 discusses some of the challenges associated with replicating the NH model outside of India. It briefly describes Shetty’s initiative to create a medical city in the Cayman Islands to capture share from the North and South American healthcare markets. It discusses some of the barriers to replicating the model in the UK and other developed markets and suggests that besides India; Africa, - despite its complexities and challenges - might offer NH growth opportunities. It also suggests that NH could play a leading role in training a new generation of healthcare professionals specifically attuned to the vast and escalating healthcare needs of developing economies, and this could be commercially valuable.
London-based financial institution CDC and a number of others think Shetty can provide the world with a new model of affirdable healthcare. In December 2015 the CDC Group, owned by the British government, with an investment portfolio valued at £2.8bn, backed NH’s initial public offering (IPO) with an investment of US$48m. The IPO valued NH at US$1bn. The issue was 8.6 times oversubscribed, with most of the demand coming from foreign institutional investors. Beside CDC, other anchor investors included the government of Singapore, Morgan Stanley, Nomura, BlackRock, and Prudential.
Dharmesh Mehta, former managing director and CEO of Axis Capital, one of the bankers to the issue, said: “We got one of the best anchor books, with several long-term investors supporting it. Investors are bullish about the Indian healthcare space, especially hospitals, and Narayana Hrudayalaya has a unique business model, and the backing of good quality management.”
In the video below Shetty argues that, “Healthcare of the future will not be an extension of the past.” Shetty has a good understanding about how technology is revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered and changing its structure and organization to such an extent that the future of healthcare will be dramatically different from what it is today. Healthcare is moving beyond the hospital towards patient self-knowledge and empowerment. Home-healthcare services facilitate enhanced doctor-patient connectivity where it had not been previously possible.
(click to play the video)
Narayana Hrudayalaya
Shetty, who has more than three decades of experience as a cardiac surgeon both in the UK and India, founded NH in 2000. Since then, it has become one of India’s leading healthcare service providers; with a network of 23 multi-specialty, primary and tertiary healthcare facilities, eight heart centers, and 25 primary care facilities, across 32 cities, towns and villages in India. Currently, NH has 5,600 operational beds, which it intends to increase to 30,000 by 2020. NH employs some 12,500 people, including 818 doctors, 5,400 nurses and about 1,660 visiting consultants.
In fiscal year 2015, Narayana provided care to nearly two million patients and undertook more than 51,456 cardiology procedures, 14,000 cardiac surgeries - which accounted for 10% of the national figure - and 184,443 dialysis procedures. Narayana posted revenues of US$219m for fiscal year 2015 and profit after tax of $2m. For the four fiscal years that ended March 31, 2015, the company’s revenues grew at a compounded annual rate of 30%.
In fiscal year 2015, Narayana provided care to nearly two million patients and undertook more than 51,456 cardiology procedures, 14,000 cardiac surgeries - which accounted for 10% of the national figure - and 184,443 dialysis procedures. Narayana posted revenues of US$219m for fiscal year 2015 and profit after tax of $2m. For the four fiscal years that ended March 31, 2015, the company’s revenues grew at a compounded annual rate of 30%.
Access to healthcare for millions of poor people
NH has one of the world’s largest telemedicine networks with 150 centers including 50 in Africa, where Shetty sees further expansion opportunities for NH. The service is free-of-charge and enhances the connectivity between remote health facilities and consultants at Narayana. Shetty, a vocal advocate of affordable healthcare, helped design the Karnataka State government Yeshasvini scheme, which is one of the largest self-funded micro healthcare insurance programs in India. It covers about 2 million people who previously did not have access to healthcare. Participants pay US$1.40 per year, which provides them with free access to over 800 surgical procedures in 400 hospitals. In the past 10 years, 85,000 peasant farmers have used the insurance to have surgery.
Challenges
NH faces some challenges. Its profit margins are low and its revenues are mainly derived from three of its largest hospitals, which concentrate on cardiac care and cardiology. As of March 2015, the company’s recent acquisitions and expansion into the Cayman Islands, where it opened a 130-bed tertiary hospital, were making losses.
However, NH’s acquisitions and expansion are strategic and their pay-offs are expected to accrue over the next four years. Also, higher yields from value-added therapies such as oncology, neurology and gastroenterology are anticipated to improve Narayana’s average revenue per operating bed (ARPOB). The company’s strategy to focus on the mid-income segment of the market is predicted to increase its utilization, given that this is a large, rapidly growing and immediately addressable market. Narayana is also advantaged by its history of efficient use of capital: it has a debt-equity ratio of only about 0.3.
Market drivers
In 2015 investors might have been influenced by the falling gold, oil and real estate markets and the relative attraction of the Indian healthcare sector, buoyed by changing demographics, rising incomes and a large and expanding middle class, greater health awareness, changes in disease profiles and a rising penetration of health insurance. By 2020 India is expected to be the world’s third largest middleclass consumer market behind China and the US. By 2030 India is projected to surpass both countries with an aggregated consumer spend of some US$13 trillion. A 2019 study by the McKinsey Global Institute (MGI) suggests that if India continues to grow at her current pace, average household incomes will triple over the next two decades, making the country the world’s fifth-largest consumer economy by 2025, up from the current 12th position.
While recognizing the challenges for India’s healthcare sector, investors must have thought that NH is well positioned to take advantage of the expected explosion in India’s middleclass consumer market. Narayana has a strong brand name and it is one of India’s leading healthcare companies, with significant revenue growth over the past four years. Its services appear cheaper than those of its competitors, such as Chennai’s Apollo Hospitals Limited, which has about four times the revenues of NH and Delhi’s Fortis Healthcare, which is about three times bigger in revenue terms. This suggests that NH has scope for substantial growth.
PART 2
International attention
Healthcare systems worldwide consume a large and escalating share of national incomes and costs and quality of care are the two most hotly debated issues among healthcare professionals. Does Shetty have an answer?
For many years, Shetty has attracted international attention. For example, in 2010 a UK prime ministerial delegation visited NH’s Medical City in Bengaluru. Vince Cable, then the UK’s Business Secretary, said: “What we're trying to do in the UK is to get more for less. Dr Shetty has shown us a model by which we do not need to accept inferior healthcare because there's less money, but actually how to get more out of the system for less resource,” Cable described his visit as “inspirational” and went on to say, "I just found it overwhelming. NH combines what we always see in a good health system, which is humane humanitarian behaviour, with sound economics."
For many years, Shetty has attracted international attention. For example, in 2010 a UK prime ministerial delegation visited NH’s Medical City in Bengaluru. Vince Cable, then the UK’s Business Secretary, said: “What we're trying to do in the UK is to get more for less. Dr Shetty has shown us a model by which we do not need to accept inferior healthcare because there's less money, but actually how to get more out of the system for less resource,” Cable described his visit as “inspirational” and went on to say, "I just found it overwhelming. NH combines what we always see in a good health system, which is humane humanitarian behaviour, with sound economics."
The Henry Ford of heart surgery
Worldwide, the demand for healthcare services is rising faster than its supply. By focusing on an endeavour to make doctors more effective, NH has demonstrated that it can deliver what healthcare systems need: enhanced patient outcomes for less money. “We have invested in infrastructure. Similar infrastructure in the UK and the US is used for about eight to nine hours a day. Ours is used for 14 to 15 hours a day, which allows us to perform the high volume of procedures,” says Shetty. In 2009 the Wall Street Journal referred to him as “the Henry Ford of Heart Surgery”.
In a similar way Henry Ford used large factories and mass-production techniques to manufacture a large number of quality cars, which many ordinary people could afford; so, Shetty developed large hospitals and a significant skill base, which he used to improve the quality of surgical procedures and reduce costs. This enabled him to offer large numbers of people access to affordable high-quality healthcare.
NH doctors, who are on fixed salaries, work in teams. Each team comprises a specialist, a number of junior doctors, trainees, nurses and paramedics. A bypass surgery typically takes about five hours. The actual grafting, which is the critical part, takes only an hour and is performed by an experienced specialist surgeon, while harvesting of the veins/arteries, opening and closing of the chest, suturing and other procedures are carried out by junior doctors. Nurses and paramedics handle the preparation and the aftercare of the patient. This Henry Ford-type process leaves the specialist free to perform more surgeries. As the volume of surgeries increase, outcomes improve, and costs are reduced. A heart surgery at NH costs less than US$2,000 per operation.
NH’s lower costs have not come at the expense of quality. Narayana’s mortality rate for coronary artery bypass procedures is 1.27% and its infection rate 1%, which are as good as that of US hospitals. Incidence of bedsores after cardiac surgery is anywhere between 8% and 40% globally, whereas at NH it has been almost zero in the last four years.
In a similar way Henry Ford used large factories and mass-production techniques to manufacture a large number of quality cars, which many ordinary people could afford; so, Shetty developed large hospitals and a significant skill base, which he used to improve the quality of surgical procedures and reduce costs. This enabled him to offer large numbers of people access to affordable high-quality healthcare.
NH doctors, who are on fixed salaries, work in teams. Each team comprises a specialist, a number of junior doctors, trainees, nurses and paramedics. A bypass surgery typically takes about five hours. The actual grafting, which is the critical part, takes only an hour and is performed by an experienced specialist surgeon, while harvesting of the veins/arteries, opening and closing of the chest, suturing and other procedures are carried out by junior doctors. Nurses and paramedics handle the preparation and the aftercare of the patient. This Henry Ford-type process leaves the specialist free to perform more surgeries. As the volume of surgeries increase, outcomes improve, and costs are reduced. A heart surgery at NH costs less than US$2,000 per operation.
NH’s lower costs have not come at the expense of quality. Narayana’s mortality rate for coronary artery bypass procedures is 1.27% and its infection rate 1%, which are as good as that of US hospitals. Incidence of bedsores after cardiac surgery is anywhere between 8% and 40% globally, whereas at NH it has been almost zero in the last four years.
It can’t be done!
“When we started our journey, we were discouraged by people saying that, ‘there is no such thing as low-cost high-quality healthcare’, and that ‘healthcare is expensive and will always be expensive’. Only when people become wealthy, they can afford quality healthcare . . . . . When I grew up, I looked at some of the richest countries in the world, struggling to offer healthcare to its citizens and quickly realized that even if India became a rich country, it still would not be able to guarantee healthcare to everyone. We had to change the way we were doing things and this is what we’ve done,” says Shetty.
Socializing the P&L
UK doctors and health providers often talk about reducing the costs of healthcare, but, says Shetty, “doctors usually have no idea how much they are spending”. In contrast, at noon every day all NH doctors receive an text with NH’s previous day’s revenue, expenses and EBIDTA (earnings before interest, depreciation, taxation and amortization). According to Dr. Ashutosh Raghuvanshi, NH’s CEO, “When you look at financials at the end of the month, it’s a post-mortem. When you look at them daily, you can do something to change things”. The daily data doctors receive describes their operations, and the various levels of reimbursement. “It’s not just a cheap process, it’s effective,” says Raghuvanshi.
In the video below Shetty suggests that a key factor for the future success of NHS England will be its ability to re-invent itself, increase its focus on costs and outcomes, benchmark key functions with successful international comparators and instil strict financial discipline in doctors, “because they represent the biggest spend in healthcare systems,” says Shetty.
In the video below Shetty suggests that a key factor for the future success of NHS England will be its ability to re-invent itself, increase its focus on costs and outcomes, benchmark key functions with successful international comparators and instil strict financial discipline in doctors, “because they represent the biggest spend in healthcare systems,” says Shetty.
(click to play the video)
Information technology
Healthcare systems require radical change at every level in order to reduce the vast and upward trajectory of unsustainable costs, improve patient experiences and outcomes, speed the translation of research into therapies and make healthcare accessible to everyone. Information technology helps in these regards. NH regularly mines data to raise the quality of care and patient outcomes. Its business intelligence activities manage real-time data on 30 different parameters that track and support efficiency improvements. Those related to clinical outcomes are then reviewed at a weekly meeting, where all major clinical procedures are discussed among doctors and best practices shared. This way NH maps the cost effectiveness of each doctor.
PART 3
Affordable quality healthcare outside India
An example of Shetty’s model of affordable quality healthcare working effectively outside of India is Narayana Health Cayman Islands. The Cayman government has given Shetty a 200-acre site and New York investors have backed him to develop and operate a Health City. In 2014 NH opened its first phase, a 130-bed tertiary hospital targeting the elective surgery markets of North and South America. “Narayana Health City Cayman will demonstrate how over-priced and inefficient US hospitals actually are and show that lower costs and better outcomes can be achieved outside of India just as well as in Bengaluru,” says Shetty.
The UK
There are numerous barriers to adopting the Shetty model in the UK and in other developed economies. NHS England has its innovators and there are efforts to roll-out innovations nationally, but they have limited success, mainly because innovations tend to be isolated and local and not widely known across different NHS functions or beyond sector boundaries. The lack of centralised expertise in NHS England skews perspectives and limits resources. This presents a significant obstacle to the adoption of compelling healthcare innovations, such as those demonstrated by Narayana.
Further, there is doctor-resistance to innovations in the UK. Doctors are trained to identify and implement proven and recommended treatment protocols for various disease states. To deviate from this is to run the risk of litigation. Further, health professionals in the UK are increasingly time-pressed, with the result that acquiring and adopting new and innovative pathways of care takes a back seat. See, Meeting the challenges of affordable quality healthcare. and, The end of doctors.
Further, there is doctor-resistance to innovations in the UK. Doctors are trained to identify and implement proven and recommended treatment protocols for various disease states. To deviate from this is to run the risk of litigation. Further, health professionals in the UK are increasingly time-pressed, with the result that acquiring and adopting new and innovative pathways of care takes a back seat. See, Meeting the challenges of affordable quality healthcare. and, The end of doctors.
Medical tourism
"Medical tourism" refers to traveling to another country for medical care. The world population is aging and becoming more affluent at rates that surpass the availability of quality healthcare resources. In addition, out-of-pocket medical costs of critical and elective procedures continue to rise, while nations offering universal care, such as the UK, are faced with ever-increasing resource burdens. These drivers are forcing patients to pursue cross-border healthcare options either to save money or to avoid long waits for treatment.
In 2015 it was estimated that the worldwide medical tourism market was between US$50bn and US$65bn and growing at an annual rate of between 15%-25%. In 2015 some 1.5 million US residents travelled abroad for care, up from 0.5 million in 2007. Two of their top destinations were Costa Rica and India. Costa Rica can yield savings on standard surgical procedures of between 45% and 65%, and India, between 65% and 90%.
Beyond the US, the OECD estimates that there are up to 50 million medical tourists worldwide annually. The most common procedures that people undergo on medical tourism trips include heart surgery, dentistry and cosmetic procedures. People are attracted to well-known, internationally accredited hospitals, which have a flow of medical tourists, internationally trained experienced health professionals, a sustained reputation for clinical excellence and a history of healthcare innovation and achievement.
Already, NH attracts medical tourists from over 50 countries, it has an international reputation for excellence, many of its top health professionals have been trained and have gained clinical experience in the US and Europe and it has a significant track record in high demand areas, particularly heart surgery. This suggests that NH is well positioned to take advantage in the future growth of medical tourism and this is probably something taken into account by NH’s anchor investors.
In 2015 it was estimated that the worldwide medical tourism market was between US$50bn and US$65bn and growing at an annual rate of between 15%-25%. In 2015 some 1.5 million US residents travelled abroad for care, up from 0.5 million in 2007. Two of their top destinations were Costa Rica and India. Costa Rica can yield savings on standard surgical procedures of between 45% and 65%, and India, between 65% and 90%.
Beyond the US, the OECD estimates that there are up to 50 million medical tourists worldwide annually. The most common procedures that people undergo on medical tourism trips include heart surgery, dentistry and cosmetic procedures. People are attracted to well-known, internationally accredited hospitals, which have a flow of medical tourists, internationally trained experienced health professionals, a sustained reputation for clinical excellence and a history of healthcare innovation and achievement.
Already, NH attracts medical tourists from over 50 countries, it has an international reputation for excellence, many of its top health professionals have been trained and have gained clinical experience in the US and Europe and it has a significant track record in high demand areas, particularly heart surgery. This suggests that NH is well positioned to take advantage in the future growth of medical tourism and this is probably something taken into account by NH’s anchor investors.
Africa
Because of entrenched obstacles to change in the healthcare systems of developed economies, Shetty has indicated an interest in Africa. In the past, private healthcare providers have neglected African healthcare; it has been underserved by governments, and mostly reliant on irregular help from abroad. However, this is about to change, and there is some evidence to suggest that healthcare reform in Africa is beginning. A 2016 African Healthcare Summit suggested that African healthcare spending is expected to grow to 6.4% of GDP in 2016, making it the second highest category of government investment. A Report from the International Finance Corporation (IFC) of the World Bank suggests that, over the next 10 years, there will be, “considerable African demand” for investment in hospitals, medicines and health professionals and meeting this demand, “can deliver strong financial returns.”
Healthcare providers also can take heart that a number of African countries are trying to establish or widen social insurance programs to give medical cover to more of their citizens. Further, there are six African countries with projected compounded annual growth rates (CAGR) for 2014 through 2017 of between 7.12% and 9.7%. These are: Rwanda, Tanzania, Mozambique, Cote d’Ivoire, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Ethiopia.
Notwithstanding, Africa is facing a dual challenge of communicable and parasitic diseases such as malaria, TB and HIV/AIDS and growing rates of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, cancer and respiratory diseases. Increased urbanisation in many African countries, along with growing incomes and changing lifestyles, have led to a rise in the rate of chronic conditions, which are projected to overtake communicable diseases as Africa’s principal health challenge by 2030. This suggests that despite the fledging signs of change, over the next decade African healthcare will still be challenged. However, over the past 15 years, NH’s has demonstrated capabilities to meet and overcome similar challenges in India, which positions it well to succeed in Africa where it already has a non-trivial telemedicine presence.
Healthcare providers also can take heart that a number of African countries are trying to establish or widen social insurance programs to give medical cover to more of their citizens. Further, there are six African countries with projected compounded annual growth rates (CAGR) for 2014 through 2017 of between 7.12% and 9.7%. These are: Rwanda, Tanzania, Mozambique, Cote d’Ivoire, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Ethiopia.
Notwithstanding, Africa is facing a dual challenge of communicable and parasitic diseases such as malaria, TB and HIV/AIDS and growing rates of chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, cancer and respiratory diseases. Increased urbanisation in many African countries, along with growing incomes and changing lifestyles, have led to a rise in the rate of chronic conditions, which are projected to overtake communicable diseases as Africa’s principal health challenge by 2030. This suggests that despite the fledging signs of change, over the next decade African healthcare will still be challenged. However, over the past 15 years, NH’s has demonstrated capabilities to meet and overcome similar challenges in India, which positions it well to succeed in Africa where it already has a non-trivial telemedicine presence.
Training health professionals
The healthcare and wellness sectors are positioned to be significant drivers of the world economy in the 21st century. Healthcare is about a US$6 trillion global market, which is increasing. Advances in medical technology, public health and governance have improved healthcare for about 30% of the world’s population. But billions of people still have no access to healthcare.
The WHO estimates that there is a shortage of nearly 13 million healthcare workers globally, but Shetty believes these shortages could be significantly higher. According to the Royal College of General Practitioners the shortage of doctors in the UK is the worst it has been for 40 years. One hundred primary care practices, serving 700,000 patients across Britain, are facing closure and the number of GP-patient consultations is estimated to rise from 338 million in 2013 to 441 million by 2017. UK experts warn that primary care doctors with too many patients will fail to provide adequate healthcare through current delivery methods and they say that this is expected to further drive patients to search online for health-related issues. See: Curing the Problems of General Practice.
Such shortages concern Shetty, who believes that the situation will only be improved with a radical change in the way healthcare is delivered. “This”, says Shetty, “will only be achieved with a change in the way health professionals are trained.” Future health professionals need to be trained for a world of e-patients. Digital classrooms will create new connections between students and health professionals and allow for access to the most current information and resources. Shetty advocates the development of a virtual global medical university, with features that include a cross-country curriculum and a reduced training period. “This is the only way we will increase the much-needed pool of healthcare talent,” says Shetty.
The WHO estimates that there is a shortage of nearly 13 million healthcare workers globally, but Shetty believes these shortages could be significantly higher. According to the Royal College of General Practitioners the shortage of doctors in the UK is the worst it has been for 40 years. One hundred primary care practices, serving 700,000 patients across Britain, are facing closure and the number of GP-patient consultations is estimated to rise from 338 million in 2013 to 441 million by 2017. UK experts warn that primary care doctors with too many patients will fail to provide adequate healthcare through current delivery methods and they say that this is expected to further drive patients to search online for health-related issues. See: Curing the Problems of General Practice.
Such shortages concern Shetty, who believes that the situation will only be improved with a radical change in the way healthcare is delivered. “This”, says Shetty, “will only be achieved with a change in the way health professionals are trained.” Future health professionals need to be trained for a world of e-patients. Digital classrooms will create new connections between students and health professionals and allow for access to the most current information and resources. Shetty advocates the development of a virtual global medical university, with features that include a cross-country curriculum and a reduced training period. “This is the only way we will increase the much-needed pool of healthcare talent,” says Shetty.
Takeaways
While change in Western healthcare systems will neither be quick nor easy, NH’s near to medium term growth will most probably come from India, the Caymans, Africa and other developing countries where the need for quality healthcare is high and growing fast, and the barriers to entry relatively low. In time, however, the US and the UK might be able to benefit from some of Narayana’s best practices so that an increasing percentage Americans may have access to high quality affordable healthcare and NHS England maybe reformed to ensure its survival.
Directory:
Tags:
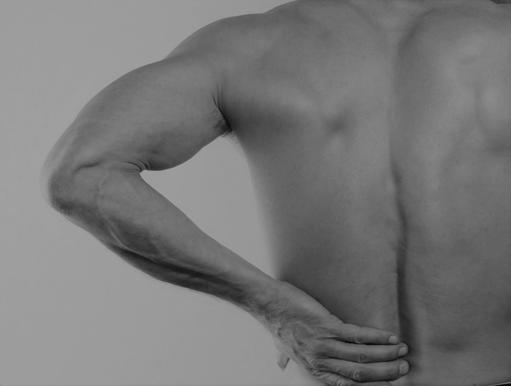
- In high-income countries populations are aging
- By 2050 the world population of people over 60 is projected to reach 2bn
- Age-related low back pain is the highest contributor to disability in the world
- Over 80% of people will experience back pain at some point in their life
- Older people with back pain have a higher chance of dying prematurely
- The causes of back pain are difficult to determine which presents challenges for the diagnosis and management of the condition
- The US $100bn-a-year American back pain industry is “ineffective”
- Each year 10,000 and 300,000 spine fusion surgeries are carried out in the UK and US respectively
- 20% of spinal fusion surgeries are undertaken without good evidence
- In 10 to 39% of spine surgery patients pain continues or worsens after surgeries
Age of the aged and low back pain
A triumph of 20th century medicine is that it has created the “age of the aged”. By 2050 the world population of people aged 60 and older is projected to be 2bn, up from 900m in 2015. Today, there are 125m people aged 80 and older and by 2050 there is expected to be 434m people in this age group worldwide. The average age of the UK population has reached 40. Some 22% will be over 65 by 2031, and this will exceed the percentage of the UK population under 25. 33% of people born today in the UK can expect to live to 100. However, this medical success is the source of rapidly increasing age-related disorders, which present significant challenges for the UK and other high-income nations. Low back pain (LBP) is the most common age-related pain disorder, and ranked as the highest contributor to disability in the world.
At some point back pain affects 84% of all adults in developed economies. Research published in 2017 in the journal Scoliosis Spinal Disorders suggests that LBP is the most common health problem among older adults that results in pain and disability. The over 65s are the second most common age group to seek medical advice for LBP, which represents a significant and increasing workload for health providers. Each year back pain costs the UK and US Exchequers respectively some £5bn and more than US635bn in medical treatment and lost productivity. LBP accounts for 11% of the total disability of the respective populations. This Commentary discusses therapies for LBP, and describes the changing management landscape for this vast and rapidly growing condition.
Your spine and LBP
Your spine, which supports your back, consists of 24 vertebrae, bones stacked on top of one another. At the bottom of your spine and below your vertebrae are the bones of your sacrum and coccyx. Threading through the entire length of your vertebrae is your spinal cord, which transmits signals from your brain to the rest of your body. Your spinal cord ends in your lower back, and continues as a series of nerves, which resemble a horse’s tail, hence its medical name, ‘cauda equine’. Between each vertebra are discs. In younger people discs contain a high degree of water. This gives them the ability to act like shock absorbers. During the normal aging process discs lose much of their water content and degenerate. Such degenerative spinal structures may result in a herniated disc when the disc nucleus extrudes through the disc’s outer fibres, or a compression of nerve roots, which may lead to radiculopathy. This is a condition more commonly known as sciatica, which is pain caused by compression of a spinal nerve root in the lower back that is often associated with the degeneration of an intervertebral disc, and can manifest itself as pain, numbness, or weakness of the buttock and outer side of the leg.
Challenges in diagnosis
Because your back is comprised of so many connected tissues, which include bones, muscles, ligaments, nerves, tendons, and joints, it is often difficult for doctors to say with confidence what causes back pain even with the help of X-rays and MRI scans. Usually, LBP does not have a serious cause. In the majority of cases LBP will reduce and often disappear within 4 to 6 weeks, and therefore can be self-managed by keeping mobile and taking over-the-counter painkillers. However, in a relatively small proportion of people with LBP, the pain and disability can persist for many months or even years. Once LBP has been present for more than a year few people return to normal activities. There is not sufficient evidence to suggest definitive management pathways for this group that accounts for the majority of the health and social costs associated with LBP.
Assessing treatment options for back pain
Ranjeev Bhangoo, a consultant neurosurgeon at Kings’ College Hospital Trust, London, and the London Neurosurgery Partnership describes the nature and role of intervertebral discs and how treatment options should be assessed.
“When a person presents with a problem in the lower back, which might manifest as leg or arm pain, you need to ask 3 questions: (i) is the history of the pain compatible with a particular disc causing the problem? (ii) Does an examination suggest that a particular disc is causing a problem? And (iii) does a scan show that the disc you thought was the problem is the problem? If all 3 answers align, then there maybe some good reason to consider treatment options. If the 3 answers are not aligned, be weary of a surgeon suggesting intervention because 90% of us will experience back pain at some point in our lives, and 90% of the population don’t need back surgery.”
Back pain requiring immediate medical attention
Although the majority of LBP tends to be benign and temporary, people should seek immediate medical advice if their back pain is associated with certain red flags such as loss of bladder control; loss of weight, fever, upper back or chest pain; or if there is no obvious cause for the pain; or if the pain is accompanied by weakness, loss of sensation or persistent pins and needles in the lower limbs. Also, people with chronic lifetime conditions such as cancer should pay particular attention to back pain.
Epidemiology of LBP
Back pain affects approximately 700m people worldwide. A 2011 report by the US Institute of Medicine, estimates that 100m Americans are living with chronic back pain, which is more than the total affected by heart disease, cancer, and diabetes combined. This represents a vast market for therapies that include surgery and the prescription of opioids. Estimates of the prevalence of LBP vary significantly between studies. There is no convincing evidence that age affects the prevalence of back pain, and published data do not distinguish between LBP that persists for more than, or less than, a year. Each year LBP affects some 33% of UK adults, and around 20% of these - about 2.8m - will consult their GP. One year after a first episode of back pain, 62% of people still experience pain, and 16% of those initially unable to work are not working after 1 year. Typically in about 60% of cases pain and disability improve rapidly during the first month after onset.
|
|


























